What Is RFID Shielding and How Does It Work
Introduction
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) technology has emerged as a highly versatile and integral component across numerous industries and everyday contexts. Its applications are extensive, encompassing asset tracking, access control, inventory management, banking, automated fare collection (AFC), toll collection, supply chain management, and various other domains.
Similar to other technologies, RFID presents certain challenges and complexities. These include issues related to interference, unauthorized access, system vulnerabilities, as well as technical intricacies arising from location and environmental factors.
However, there are methods to address these limitations.
Imagine This Scenario:
You’re standing in a crowded subway. Unbeknownst to you, someone nearby waves a small device near your pocket. In seconds, they’ve skimmed your credit card information without even touching you — all thanks to RFID technology.
This is where RFID shielding steps in as a silent protector.
What Is RFID and RFID Shielding?
RFID stands for Radio Frequency Identification, a technology that uses radio waves to wirelessly identify and track objects.
RFID shielding (often referred to as RFID blocking) refers to the materials or methods used to block or reduce RFID signals, protecting sensitive data from being read by unauthorized devices and blocking interference. RFID blocking products, such as wallets, sleeves, passport covers, shielding enclosures and shield fabrics are practical applications of RFID shielding designed for various industrial use cases and everyday personal security.
In this blog, we’ll explore what RFID shielding and RFID blocking are, why they are important, and how they work across different industries and in our daily lives. Let’s dive in.
Understanding RFID Basics
Before we discuss shielding, it’s helpful to understand how RFID works.
What Is RFID?
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a technology that allows information to be transmitted wirelessly between a tag and a reader using radio waves.
Core Components:
- RFID Tags: Small devices containing data. They can be embedded in credit cards, passports, clothes, and countless other items.
- RFID Readers: Devices that send out radio waves and read data from nearby tags.
- Antennas: Components that send and receive radio signals between the reader and tags.
How Does RFID Work?
When an RFID tag enters the electromagnetic field of a reader, it absorbs energy from the reader’s signal. Using that energy, the tag transmits its stored data back to the reader through radio waves. The reader then collects and processes this data for identification or tracking purposes.
What Is RFID Shielding?
RFID shielding is a technique used to block or minimize radio waves, preventing RFID tags from being read when they shouldn't be. RFID blocking products apply this principle to safeguard personal data against unauthorized scans.
Think of it like this:
A Faraday cage blocks electric fields entirely: Just as a Faraday cage prevents electric currents from penetrating its enclosure, RFID shielding creates a barrier that blocks radio frequencies from reaching RFID tags.
Noise-cancelling headphones reduce unwanted sounds: Like how noise-canceling headphones block background noise, RFID shielding reduces unwanted RFID signals, ensuring that only desired communications occur between tags and authorized readers.
Similarly, RFID shielding keeps unwanted radio signals out or keeps signals contained:
This helps to prevent accidental or malicious scanning by restricting where and how RFID tags can be read, a principle often used in RFID-blocking wallets and sleeves.
The Purpose of RFID Shielding
Access Control: It ensures that only authorized RFID readers can communicate with tags, preventing unauthorized personnel from accessing secured data or areas.
Interference Management: In environments with multiple RFID readers, shielding minimizes signal overlap, reducing errors caused by unintended or cross-reader scans, and maintaining accurate data collection.
Why RFID Shielding Is Important

Security & Privacy
RFID shielding and RFID blocking protect sensitive personal data by preventing unauthorized scanners from skimming information stored on credit cards, passports, or ID badges. This helps individuals avoid identity theft and financial fraud caused by hidden, malicious readers.
Operational Integrity
In busy environments like warehouses, retail stores, or hospitals, RFID shielding prevents scanners from unintentionally reading tags located in adjacent areas. This ensures accurate inventory tracking and smooth workflow management without accidental data collection from unrelated zones.
Interference Mitigation
With multiple RFID readers operating in close proximity, signals can overlap, causing cross-talk and reading errors. RFID shielding minimizes these unwanted interactions, maintaining system accuracy and preventing data duplication or misreads during operations.
Enhanced Asset Protection
For high-value or sensitive assets, RFID shielding ensures that tracking information is only accessible to authorized personnel. This prevents external parties from identifying, tracking, or targeting valuable inventory or confidential equipment through unauthorized RFID scans.
Improved System Efficiency
By limiting unintended reads, RFID shielding improves the overall efficiency of RFID systems. It reduces data noise, allowing systems to process clean, accurate information faster, and minimizing the need for manual data corrections or system recalibrations.
How RFID Shielding Works
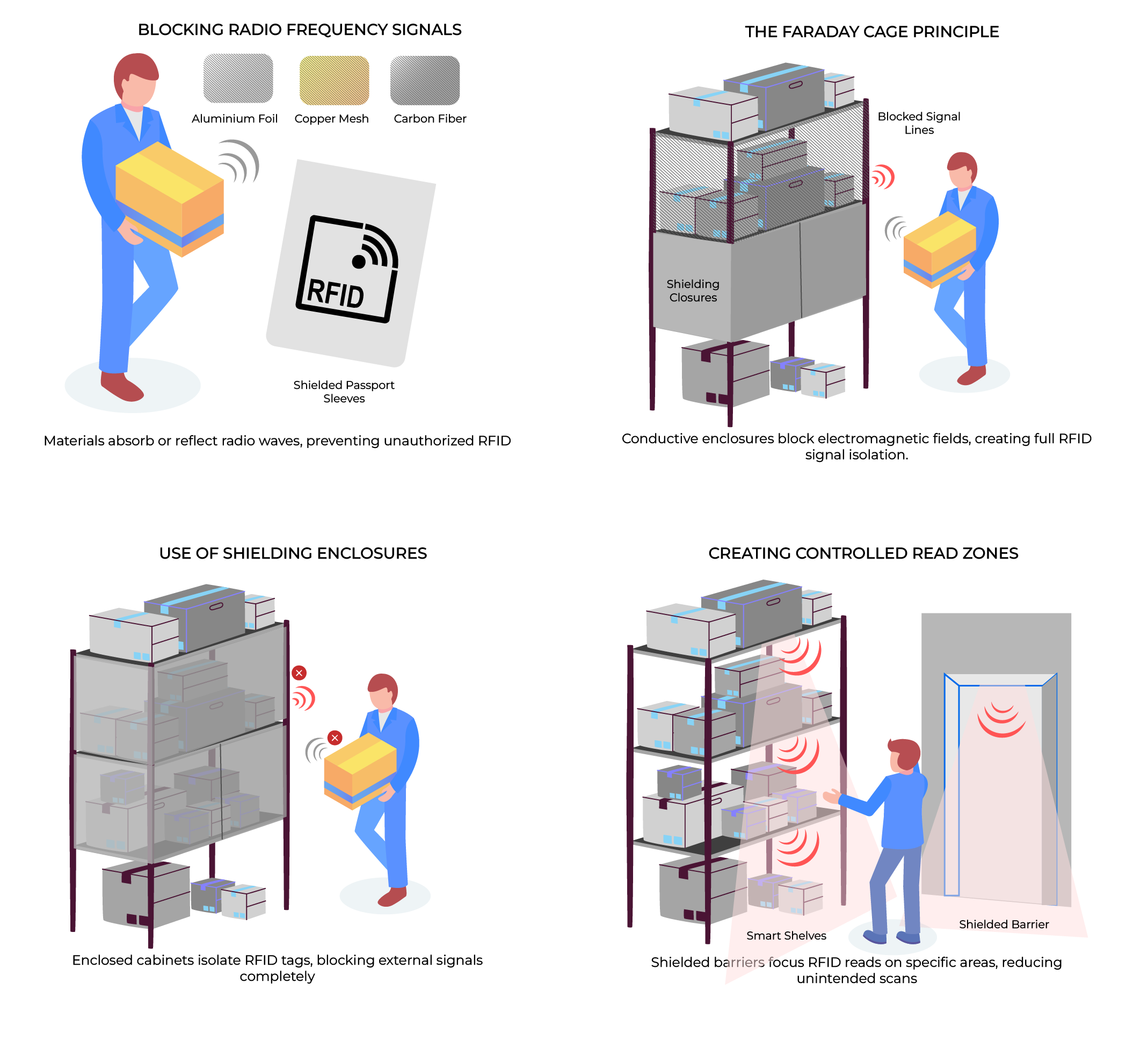
1. Blocking Radio Frequency Signals
Shielding materials such as aluminum, copper, and carbon fiber absorb or reflect radio waves, stopping them from reaching RFID tags. This is the core principle behind RFID blocking wallets, shielding bags for passports, and protective sleeves for contactless cards.
2. Creating Controlled Read Zones
In warehouses, retail stores, and industrial settings, shielded barriers or enclosures limit where RFID tags can be read. Smart shelves and entry portals use precise shielding to focus read zones, ensuring only the intended tags within a specific area are scanned.
3. Use of Shielding Enclosures
Shielded cabinets, containers, or storage bins fully isolate RFID tags, preventing unauthorized or accidental reads outside designated areas. These enclosures are commonly used in laboratories, data centers, logistics hubs, and secure transport applications to safeguard sensitive assets.
4. The Faraday Cage Principle
A Faraday cage is a conductive enclosure that blocks both electric and magnetic fields. In RFID environments, it’s applied to create fully shielded rooms, cabinets, or containers where no RFID signals can penetrate, ensuring complete signal isolation.
5. Software-Aided Shielding
Without using physical barriers, RFID systems can adjust reader settings like power levels, antenna positioning, and scanning intervals. This form of virtual shielding controls the effective read range, minimizing unintended scans while maintaining operational efficiency and flexibility.
Types of RFID Shielding Solutions
Personal Protection Products
Everyday, users rely on RFID blocking products like wallets, card sleeves, and passport covers to safeguard personal data from electronic pickpocketing. These portable solutions prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information stored on contactless credit cards, IDs, and travel documents while remaining lightweight and easy to use.
Industrial Use Cases
In industrial environments, shielded enclosures, transport bins, and secure storage cabinets protect valuable assets and sensitive data during production, testing, and transportation. These solutions prevent cross-zone scanning, maintain data integrity, and ensure only authorized equipment or personnel can access the tagged items, improving operational security.
Retail and Logistics Applications
Retailers and logistics providers use smart shelves with directional antennas and shielding curtains to create controlled reading zones. These setups ensure accurate inventory tracking by focusing RFID reads on specific shelf levels or storage zones, reducing read errors and improving stock management efficiency throughout the supply chain.
Dock Doors Equipped with Shielding
At loading docks and warehouse entrances, RFID shielding is installed around dock doors to concentrate reads only on tagged items entering or leaving the facility. This focused approach minimizes stray reads from nearby storage areas and ensures precise tracking of inbound and outbound shipments.
Healthcare & Government
Healthcare facilities and government agencies utilize shielded badge holders to protect sensitive access credentials from unauthorized scanning. Additionally, shielded storage rooms and containers are used to secure medical devices, pharmaceuticals, and classified government assets, ensuring privacy, compliance, and protection against potential security breaches.
Materials Used in RFID Shielding
Metals
Materials like aluminium, copper, and stainless steel are highly effective at blocking and reflecting radio waves. These metals create strong barriers that prevent RFID signals from passing through, making them ideal for enclosures, cabinets, and industrial shielding applications requiring high levels of protection.
Conductive Fabrics
Conductive fabrics are woven with fine threads of silver, copper, or other conductive materials. These fabrics are lightweight, flexible, and easily incorporated into personal protection products like RFID blocking wallets, sleeves, and clothing, providing portable shielding against unauthorized RFID scans in daily life.
Composite Materials
Composite materials combine multiple layers of shielding elements, including carbon-infused polymers and laminates. They offer advanced protection for high-security environments such as military and government facilities, providing both durability and superior signal blocking across a wide range of RFID frequencies.
Common Applications of RFID Shielding
Retail
In retail stores, RFID shielding is used to prevent accidental reads during checkout or inventory audits by isolating scanning zones. Smart shelves and shielded checkout counters help manage dense RFID environments, ensuring accurate inventory counts and avoiding misreads. For example, clothing stores use shielded fitting rooms to avoid scanning nearby items unintentionally.
Finance & Travel
RFID blocking wallets and passport sleeves protect contactless credit/debit cards and e-passports from unauthorized scans. These personal protection products prevent electronic pickpocketing and identity theft while traveling or in crowded public spaces like airports, subways, or shopping malls, where hidden scanners can attempt to steal sensitive personal and financial data.
Warehousing & Manufacturing
In warehouses and manufacturing plants, shielded bins, cages, or enclosures are used to separate RFID-tagged items within different workflows or departments. This prevents cross-reading of tags from adjacent workstations, ensuring correct tracking of inventory, tools, and parts. For example, automotive assembly lines often use shielded racks for parts staging.
Military & Government
Military and government organizations use RFID shielding to protect classified data stored on sensitive devices and documents. Shielded rooms, secure containers, and badge holders ensure that only authorized personnel can access secure areas or equipment. For example, shielded briefcases are used to transport classified files without the risk of remote data access.
Best Practices for Implementing RFID Shielding
1. Conduct a Site Survey
Before installation, evaluate the facility to identify locations where interference, cross-reads, or unauthorized scans may happen. For example, in warehouses, analyze dock doors, storage zones, and workstations to determine where RFID blocking or shielding is necessary for accurate tracking.
2. Select the Right Materials
Choose shielding materials based on the RFID frequency (LF, HF, UHF, or microwave) being used. For example, aluminium may work well for UHF applications, while conductive fabrics may be better suited for HF applications like contactless credit cards and ID badges.
3. Test and Validate
After installation, perform regular testing to verify that the shielding remains effective. Over time, wear, damage, or environmental changes can reduce shielding performance, so routine validation ensures ongoing protection and system accuracy.
4. Combine with Access Control
Enhance security by pairing RFID shielding with authentication systems such as key cards, PIN codes, or biometrics. This layered approach ensures that even if a signal bypasses shielding, only authorized users can access sensitive information or secure areas.
Conclusion
RFID technology offers unmatched convenience and efficiency, but without proper controls, it can expose sensitive information and disrupt operations. RFID shielding serves as a crucial safeguard, ensuring data privacy, system stability, and compliance.
As RFID continues to grow in industries like retail, healthcare, logistics, and personal security, investing in proper shielding solutions is no longer optional — it’s essential.
FAQs
Q1. What is RFID shielding?
RFID shielding refers to the use of materials or methods to block or reduce radio-frequency signals, preventing unauthorized access to RFID tag data and minimizing interference in RFID systems.
Q2. Why is RFID shielding important?
RFID shielding helps protect sensitive information from unauthorized scans, prevents accidental reads, reduces system interference, and ensures accurate data collection in environments with multiple RFID readers.
Q3. How does RFID shielding work?
RFID shielding works by using conductive materials like aluminum, copper, or special fabrics to absorb or reflect radio waves, stopping them from reaching RFID tags or readers.
Q4. What is the difference between RFID shielding and RFID blocking?
The terms are often used interchangeably. RFID blocking usually refers to personal products like wallets and sleeves, while RFID shielding covers both personal and industrial solutions to control RFID signal exposure.
Q5. Where is RFID shielding commonly used?
RFID shielding is used in retail, logistics, healthcare, finance, travel, military, and government sectors to secure data, manage inventory accurately, and prevent unauthorized scanning.
Q6. What materials are used for RFID shielding?
Common materials include metals like aluminum and copper, conductive fabrics woven with silver or copper threads, and composite materials like carbon-infused polymers for advanced applications.
Recent Posts
-
What Is RFID Shielding and How Does It Work
Introduction Radio-frequency identification (RFID) technology has emerged as a highly versatile and …Jun 25th 2025 -
The Use Cases of RFID in Healthcare: Enhancing Efficiency, Safety, and Patient Care
Introduction In the modern medical landscape, healthcare providers continually seek ways to enhance …Jun 19th 2025 -
Zebra Handheld RFID Readers Comparison: MC3330xR, MC3390xR, RFD40 Series, RFD9090, & RFD9030
Introduction Zebra Technologies stands as a global leader in enterprise asset intelligence, offering …Jun 13th 2025




